What is Peripheral
Vascular and Arterial Disease?
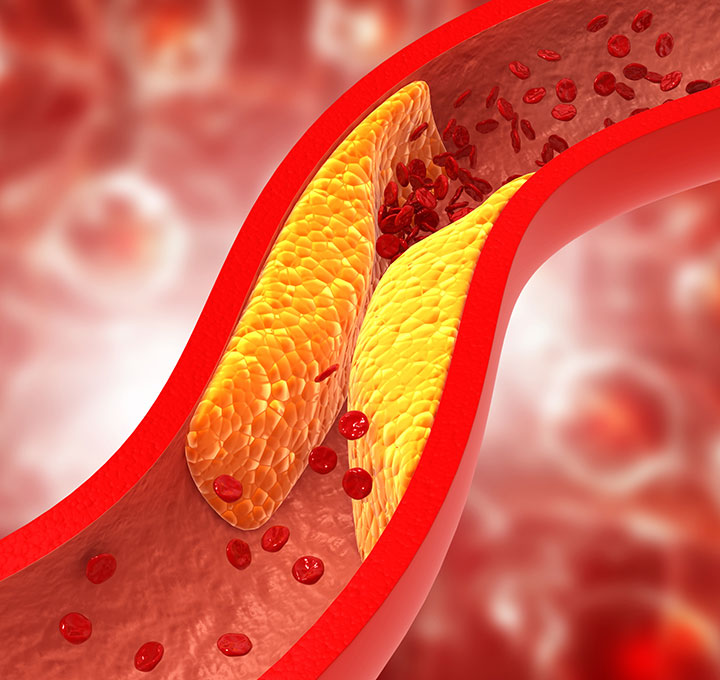
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) refers to arterial disease that occurs outside of the heart or brain. In PAD, arteries that carry oxygenated blood throughout the body become narrowed or even blocked, usually because of atherosclerosis or plaque. PAD most commonly affects the arteries in the legs, but it also can involve arteries that carry blood to the head, arms, kidneys and gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms can range from severe leg pain when walking, all the way down to extremely mild or nonexistent. Other symptoms can include sores that will not heal and a persistent feeling of coldness throughout the legs and feet.
Peripheral Vascular and
Arterial Disease Treatment
Angioplasty, with or without vascular stenting, is a minimally-invasive procedure used too improve blood flow when a vein or artery is too narrow or even blocked. In angioplasty, live x-ray called fluoroscopy is used to guide a balloon-tipped catheter into the narrowed or blocked artery or vein. The balloon is slowly inflated to open the vessel, then deflated and removed. A metal mesh tube called a stent may be permanently placed in the newly opened vessel to help keep it open.
